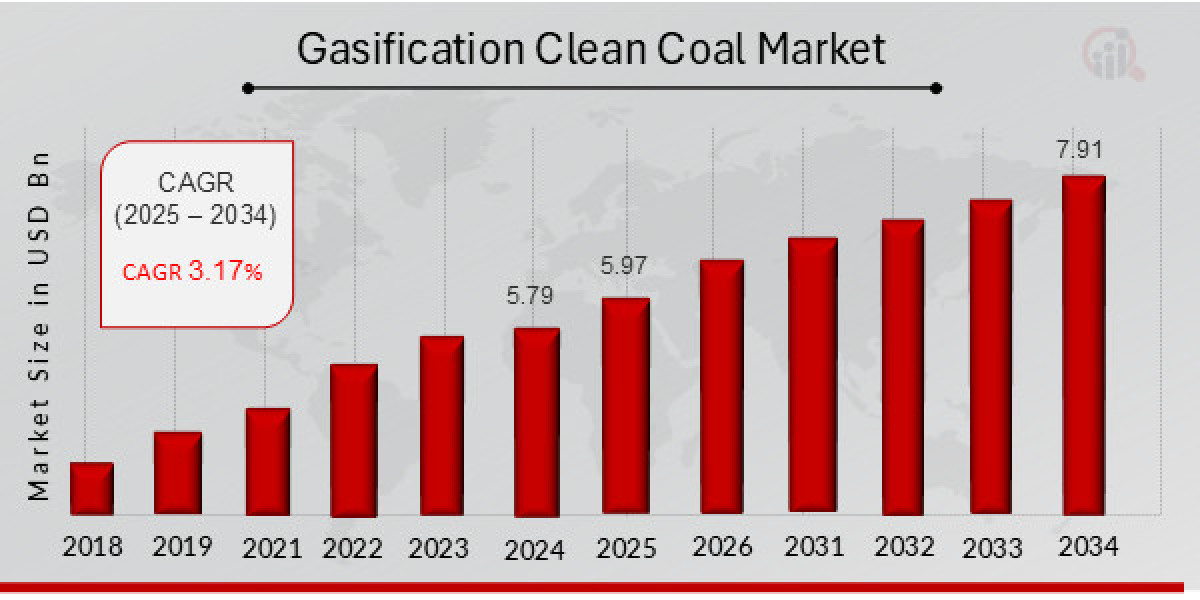
The gasification clean coal market is experiencing steady growth as global energy strategies increasingly focus on reducing carbon emissions while maximizing energy security. Gasification, a clean coal technology, is gaining prominence for its ability to convert coal into cleaner synthetic gas (syngas) used in power generation, chemicals, and liquid fuels, while minimizing pollutants compared to traditional coal combustion.
As global energy demands rise and decarbonization targets tighten, countries are investing in clean coal infrastructure to support a balanced, transitional energy mix. The versatility of gasification in supporting industrial, power, and transportation sectors while complying with environmental standards makes it a cornerstone of future-ready energy systems.
Market Dynamics
1. Growing Global Energy Demand
Increasing energy consumption—especially in emerging economies—continues to drive investment in diversified and stable energy sources. Coal remains a vital part of the energy mix in countries like China, India, South Africa, and Indonesia due to its availability and cost advantages. Gasification offers these regions a path to cleaner coal utilization by reducing emissions and increasing efficiency.
Power utilities are using gasification technology to generate electricity with lower sulfur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), and particulate emissions compared to conventional plants.
2. Emission Control and Environmental Regulations
Tighter emissions regulations, such as those mandated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), European Union Green Deal, and China's Air Pollution Prevention Act, are pushing energy producers to adopt low-emission technologies. Clean coal gasification aligns with these goals by enabling carbon capture and storage (CCS), reducing reliance on high-emission power systems.
Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle (IGCC) systems are being promoted for their high efficiency and potential to integrate CCS, making them attractive to environmentally conscious governments and utility providers.
3. Chemical and Liquid Fuel Applications
Beyond electricity, gasification enables coal to be transformed into syngas used in producing fertilizers, methanol, diesel, and other chemicals. This versatility opens up multiple revenue streams and justifies large-scale gasification projects, especially in coal-rich nations.
Coal-to-liquid (CTL) and coal-to-chemical (CTC) plants using gasification are being developed to reduce crude oil imports and enhance domestic energy security in countries like China and India.
4. Technological Advancements and Efficiency Gains
Modern gasification systems are more compact, efficient, and environmentally sustainable. Advances in feedstock flexibility (supporting biomass and waste co-gasification), automated controls, and improved reactor designs are reducing operational costs and improving syngas yields.
Innovation in pre-treatment methods and oxygen-blown gasifiers are further optimizing the performance of gasification systems in large-scale applications.
Competitive Landscape
The gasification clean coal market is moderately competitive, with key global players focusing on technology innovation, partnerships, and project financing to expand their footprint.
Key Players and Strategic Developments
- General Electric, Siemens Energy, and Shell offer advanced gasification technologies like IGCC and dry-feed gasifiers tailored for power and industrial applications.
- KBR Inc. and Air Products and Chemicals are known for their proprietary syngas production systems and are involved in integrated clean coal projects globally.
- China Shenhua Energy and Synthesis Energy Systems are leading gasification project developers in Asia, with a strong presence in CTL and CTC sectors.
These companies are focusing on commercial-scale deployments, long-term supply agreements, and strategic alliances with national governments and utilities to ensure long-term market presence.
Regional Diversification
Global leaders are localizing production and services to comply with regulatory frameworks and to access low-cost labor and coal. For example, Chinese companies have built several large gasification hubs tailored to regional fuel specifications and environmental goals.
Joint ventures between Western technology providers and Asian energy firms are enabling technology transfer and capacity building in developing regions.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the global gasification clean coal market, driven by China and India’s reliance on coal and their need for cleaner energy alternatives. Both countries are investing heavily in CTL and CTC projects to reduce energy imports and improve environmental performance.
Government subsidies, domestic manufacturing, and policy support have created favorable conditions for market expansion across Southeast Asia.
North America
The U.S. is focusing on reviving coal in a sustainable way through gasification and carbon capture. Several demonstration projects backed by the Department of Energy are testing advanced IGCC systems integrated with CCS and hydrogen production capabilities.
Canada is exploring gasification in oil sands operations and remote regions where conventional power infrastructure is lacking.
Europe
While Europe is phasing out traditional coal, clean coal gasification is being considered for industrial heat and synthetic fuel generation in select regions. Countries like Germany, Poland, and the Netherlands are exploring hybrid systems integrating waste and coal feedstocks.
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- High Capital Costs: Gasification plants require significant upfront investment, often supported only by government grants or public-private partnerships.
- Policy and Public Resistance: Environmental advocacy groups continue to oppose any coal-based systems, despite the cleaner nature of gasification.
- Complex Engineering: Operating and maintaining a gasification plant requires highly skilled labor and robust supply chains, which can pose scalability challenges.
Opportunities
- Carbon Capture Integration: IGCC systems with CCS are emerging as a bridge to zero-carbon energy, providing utilities with a path to comply with future net-zero mandates.
- Hydrogen Production: Syngas from coal gasification can be used to produce blue hydrogen, opening a new market opportunity in hydrogen energy strategies.
- Waste Co-Gasification: Integrating biomass and municipal waste into gasifiers enables circular economy models while reducing fossil feedstock reliance.
Conclusion
The gasification clean coal market is gaining momentum as nations seek to balance energy reliability, environmental responsibility, and economic growth. With the flexibility to produce power, fuels, and chemicals from abundant coal reserves—while dramatically reducing emissions—gasification is set to play a crucial role in the global clean energy transition. As technological advancements continue and policy frameworks mature, the market is expected to expand into new sectors and geographies.
To explore full insights and future growth opportunities, access the comprehensive gasification clean coal market report.
More Trending Reports: