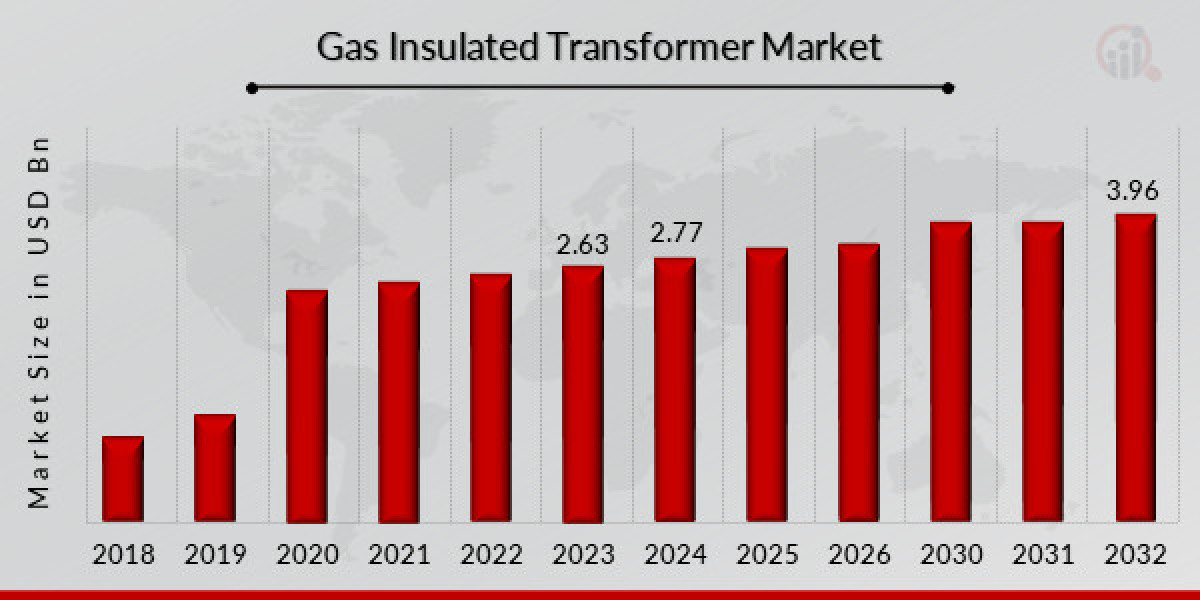
The gas insulated transformer market is witnessing significant growth fueled by increasing demand for compact, high-efficiency power transmission equipment. As urban infrastructure expands and global electricity consumption soars, gas insulated transformers (GITs) are becoming the preferred choice for utilities, substations, and industrial applications due to their superior performance in constrained and high-risk environments.
Market Dynamics
Gas insulated transformers are electrical transformers that use sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆) gas for insulation instead of traditional oil-based systems. These systems offer high reliability, compact design, fire safety, and reduced maintenance—features that are especially valuable in urban, underground, offshore, and high-voltage environments.
One of the primary market drivers is the growing demand for space-efficient power solutions in densely populated cities. With limited availability of land for large substations, GITs allow utilities to install powerful transformers in compact underground or indoor setups, enabling efficient energy distribution without expanding land usage.
As nations invest in modernizing their electric grids, gas insulated transformers are emerging as a key component of smart, resilient infrastructure. Countries across Asia-Pacific, Europe, and the Middle East are upgrading aging transmission systems to handle increasing loads, renewable energy integration, and advanced grid management requirements. GITs support high-voltage transmission with minimal energy losses, helping utilities meet efficiency targets.
The global shift toward renewable energy is another significant catalyst. Wind and solar farms, often located in remote areas or offshore, require robust and space-conscious transformers that can operate under harsh environmental conditions. Gas insulated transformers offer the durability and safety needed in such deployments, especially for floating wind installations and marine substations.
Moreover, regulatory emphasis on environmental safety and operational reliability is boosting adoption. Unlike oil-filled transformers that pose fire hazards and risk of contamination, GITs offer sealed, maintenance-free operation. Though SF₆ gas has a high global warming potential, manufacturers are increasingly offering low-leakage designs and alternative gas technologies to align with environmental standards.
Electrification initiatives in developing economies also create long-term growth potential. From railway electrification to data center expansions and industrial automation, the need for stable, compact, and efficient power transformers continues to grow.
Competitive Landscape
The gas insulated transformer market is marked by robust competition and rapid technological advancement. Leading manufacturers include ABB, Siemens Energy, Mitsubishi Electric, General Electric (GE), and Hyundai Electric.
ABB offers a wide range of gas insulated transformers with digital monitoring and eco-efficient options that cater to smart grid projects and compact substations. Siemens Energy has been pioneering vacuum-insulated and alternative gas technologies that reduce SF₆ use while maintaining performance and safety standards.
Mitsubishi Electric continues to focus on developing compact, high-voltage transformers for large infrastructure and transportation projects. GE has made significant investments in digital asset management platforms that integrate with its GIT systems to provide predictive analytics and lifecycle optimization.
Hyundai Electric is expanding its footprint in Asia and the Middle East by offering cost-competitive, high-performance GITs tailored to regional grid specifications and climate conditions.
Regional players in China, India, and Southeast Asia are emerging rapidly due to strong local demand and supportive industrial policies. These companies are developing standard and custom GITs for power distribution companies and large infrastructure projects, often leveraging government-backed R&D and manufacturing incentives.
Innovation in materials, gas alternatives, and digital integration continues to define the competitive landscape. Companies are exploring SF₆ alternatives such as fluoronitrile blends and nitrogen-based insulators to comply with tightening emissions regulations. Additionally, advanced sensors and AI-based monitoring tools are being integrated to detect insulation breakdown, pressure fluctuations, and other potential faults in real time.
Strategic partnerships and long-term service agreements are becoming vital as utilities seek turnkey solutions that offer not only equipment but also installation, diagnostics, and maintenance over the asset’s lifecycle.
Opportunities and Outlook
The future of the gas insulated transformer market is closely tied to the broader shift toward clean energy, urbanization, and digital infrastructure. As governments allocate more funding toward renewable integration and smart grid development, demand for compact and efficient transformer systems is expected to surge.
Opportunities are expanding in offshore renewable projects, where space constraints and environmental exposure necessitate rugged and compact transformer designs. GITs also present an ideal solution for urban railways, metros, and underground substations—particularly in cities pursuing carbon neutrality goals and sustainable urban planning.
The adoption of digital twins and remote monitoring is opening new avenues for service providers. Utilities are increasingly interested in condition-based maintenance and real-time performance tracking, which reduce downtime and operational risks. Companies offering integrated software-hardware solutions will gain a competitive edge in long-term infrastructure partnerships.
Environmental innovation will also play a pivotal role. As pressure mounts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, manufacturers offering SF₆-free or low-emission GIT alternatives are expected to benefit from policy support and market preference. This shift represents both a challenge and a chance for established players and new entrants alike to drive product differentiation and market share.
Despite high initial costs, the long-term savings in land, maintenance, and safety make GITs a strategic investment, especially for infrastructure projects with complex installation constraints. With electric grids evolving rapidly, the role of advanced transformer systems is set to become even more central to energy system resilience and efficiency.
Conclusion
The gas insulated transformer market is poised for significant growth as urbanization, electrification, and grid modernization demand smarter, safer, and more efficient power transmission systems. With strong investment in renewables, infrastructure, and digital grid management, GITs are becoming indispensable to next-generation energy networks. As competition intensifies, innovation and sustainability will remain key drivers of market leadership.
Explore detailed forecasts and global trends at Market Research Future.
More Trending Reports: