Understanding Gutter Downspouts: Importance, Types, and Maintenance
Gutter downspouts are necessary components of any roof, playing a crucial function in managing rainwater and protecting residential and commercial structures from water damage. This post will explore the importance of gutter downspouts, the numerous types available, and key maintenance tips to guarantee they function efficiently.
The Importance of Gutter Downspouts
Gutter downspouts are vertical pipes that direct rainwater collected by gutters far from the structure of a structure. These systems help prevent a wide variety of problems, including:
- Foundation Erosion: Without appropriate drainage, water can pool around the structure of a building, resulting in soil disintegration and possible structural damage.
- Basement Flooding: Excess water can leak into basements, causing flooding that may lead to costly repairs and a conducive environment for mold growth.
- Landscape Damage: Inefficient drainage can lead to soil disintegration in gardens and lawns, adversely impacting plant health and landscaping integrity.
- Wall and Roof Damage: Improperly routed rainwater can hurt siding, roofing products, and lead to wood rot, which even more adds to structural deterioration.
Due to these considerable functions, property owners and home supervisors need to pay very close attention to gutter downspout design and maintenance.
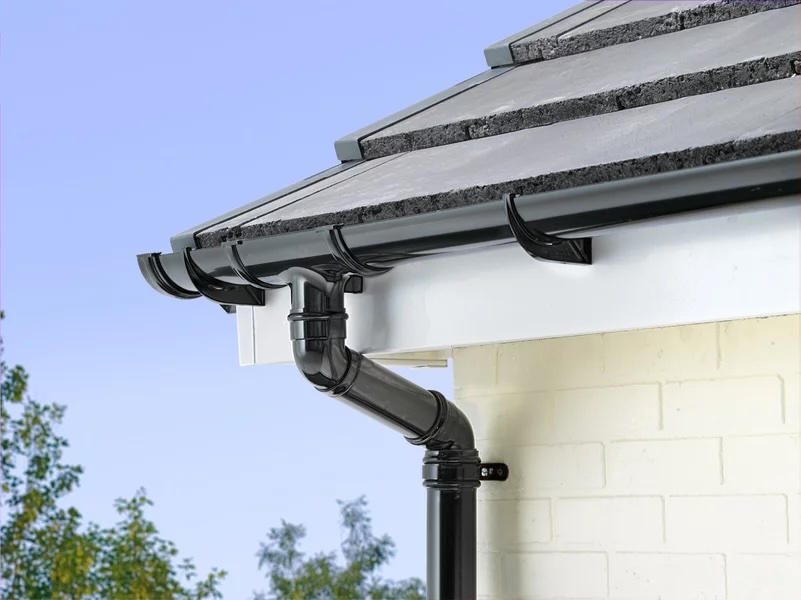

Kinds Of Gutter Downspouts
There are a number of kinds of gutter downspouts offered, each serving specific purposes based on the architecture of the building and the volume of water overflow.
1. Standard Downspouts
The most common type, basic downspouts, are typically rectangle-shaped or round and are connected straight to the gutter system. These are typically made from:
- Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to deterioration.
- Vinyl: Affordable and easy to install, though less long lasting than metal alternatives.
- Steel: Very long lasting but can rust without a protective surface.
2. Leader Pipes
Leader pipelines are typically utilized in combination with standard downspouts to redirect water away from developing structures in locations with heavy rainfall. They're generally larger than basic downspouts and developed for high-capacity drainage.
3. Extensions and Diverters
Extensions and diverters are extra parts used with downspouts to control the instructions of the water flow. They can direct water further far from the structure or into rain barrels for harvesting, lowering waste.

4. Crushed Stone Drainage Systems
These systems integrate crushed stone to assist distribute water more equally across areas of landscaping, reducing erosion and enabling the ground to absorb more rainwater.
5. Rain Barrels
Rain barrels are frequently linked to downspouts, making it possible for house owners to collect and save rainwater for later use in irrigation, helping save water and minimize energy expenses.
| Type | Description | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Most typical, direct water from gutters. | Aluminum, Vinyl, Steel |
| Leader Pipes | High-capacity systems for heavy rains. | Varies (metal/plastic) |
| Extensions | Modifies instructions of water flow away from structure. | Plastic, Metal |
| Crushed Stone | Diffuses water across landscaped locations. | Crushed Stone, Gravel |
| Rain Barrels | Collects runoff for watering and water conservation. | PVC, Plastic, Wood |
Maintaining Gutter Downspouts
Regular maintenance of gutter downspouts is crucial to avoid blockages and ensure that water is directed far from the structure efficiently. Here are some essential tips:
1. Routine Cleaning
Debris such as leaves, twigs, and dirt can accumulate in downspouts, causing clogs. It is recommended to:
- Clean at least two times a year: Once in spring and as soon as in fall.
- Utilize a garden trowel: Remove big debris lodged in the downspout.
- Use a pipes snake: For persistent blockages, a snake can assist remove any accumulated product.
2. Check for Damage
- Look for rust: Metal downspouts ought to be examined for indications of corrosion.
- Try to find bends or kinks: Ensure that the downspout is straight to enable appropriate drainage.
- Analyze joints and seals: Cracks or loose fittings may require sealing or replacement.
3. Guarantee Proper Alignment
Downspouts ought to be positioned to allow for gravity-assisted drainage:
- Use a level: Ensure they slope away from the structure at a small angle.
- Change extensions: If they divert water towards the structure instead of away from it.
4. Consider Seasonal Preparation
In areas with freezing temperatures, property owners should:
- Winterize downspouts: Clear any water or ice to avoid freezing and subsequent damage.
- Install heated cable televisions: These can avoid ice dams in cooler environments.
FAQs about Gutter Downspouts
Q1: How often should I clean my gutter downspouts?
A1: It is advised to clean your gutter downspouts at least two times a year, ideally in spring and fall, however more frequently if your home is surrounded by trees.
Q2: What can I do if my downspouts are clogged?
A2: You can eliminate debris by hand with a trowel or use a pipes snake to clear blockages. If the problem continues, consider working with a professional service.
Q3: Is it required to install extensions on downspouts?
A3: Extensions are helpful as they assist direct water further away from the foundation, minimizing the risk of erosion and damage.
Q4: Can I set up gutter downspouts myself?
A4: Yes, many homeowners can install gutter downspouts using easily available products and tools; however, if you're not sure, working with a professional may guarantee compliance with local building regulations.
Q5: How do I know if my gutter downspouts are working properly?
A5: Observe the water flow throughout and after rainfall; if water is pooling around the foundation or backing up in the gutters, it may suggest a problem with the downspouts.
Gutter downspouts are vital in an extensive drainage system, safeguarding buildings from potential catastrophes brought on by water damage. Understanding the kinds of downspouts available and their maintenance requires can boost their effectiveness and longevity. Routine inspections and proper care will guarantee that these elements perform their necessary functions, safeguarding both the structure and surrounding landscape successfully.